
The Canadian cannabis landscape, marked by its dynamic evolution, places a fundamental element at the forefront of discussions – the Endocannabinoid System (ECS). At its core, the ECS is an intricate network comprising receptors, endocannabinoids, and enzymes, orchestrating a delicate balance within the body. The significance of comprehending the nuances of the ECS is amplified, particularly within the realm of cannabis consumption, where its intricate dance with the cannabinoids present in the plant comes to the forefront. This direct interaction, predominantly facilitated by cannabinoids like THC and CBD, extends its influence across a spectrum of biological functions, underscoring the far-reaching implications of the ECS.
Delving deeper into the realms of ECS unveils a multifaceted impact, resonating through crucial aspects of physiological well-being. The sway it holds over brain receptors, the regulatory role it plays in biological functions such as eating and metabolism, and its intricate involvement in areas like anxiety, memory, learning, and reproduction accentuate its paramount importance. Against this backdrop, the objective of this article is to furnish a comprehensive guide to the ECS, acting as an illuminating resource for individuals navigating the Canadian cannabis market. By shedding light on the profound interplay between the ECS and cannabis, we aim to empower readers with insights into how this symbiotic relationship influences various facets of health and wellness in the Canadian context.
The Basics of the Endocannabinoid System
Embarking on an exploration of the foundational aspects of the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) reveals a complex but fascinating orchestration within the human body. The ECS is essentially a regulatory network comprised of three primary components: endocannabinoids, receptors, and enzymes. Endocannabinoids, such as anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), act as signaling molecules that bind to cannabinoid receptors, initiating a cascade of responses. These receptors, notably CB1 and CB2, are distributed throughout the body, with CB1 predominantly found in the central nervous system and CB2 more prevalent in the peripheral tissues and immune cells.
Enzymes within the ECS, particularly fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL), are responsible for the synthesis and degradation of endocannabinoids, tightly regulating their levels. This dynamic interplay of endocannabinoids binding to receptors and enzymes modulating their concentrations underscores the pivotal role of the ECS in maintaining homeostasis, or internal balance, within the body.
The ECS’s homeostatic function extends across a spectrum of physiological processes, including mood, sleep, appetite, immune response, and more. It acts as a harmonizing force, dynamically adjusting to internal and external stimuli to ensure optimal functioning. Understanding these fundamental aspects of the ECS sets the stage for a more profound comprehension of how cannabis, with its phytocannabinoids mirroring endocannabinoids, can impact this intricate system and contribute to overall well-being.
ECS and Brain Receptors
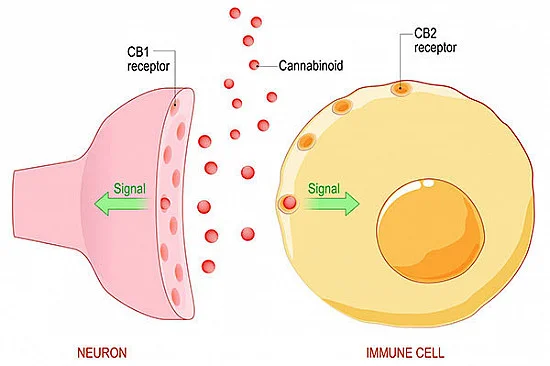
Delving into the intricate world of the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) unveils a fascinating story of communication primarily facilitated through two key receptors: CB1 and CB2. CB1 receptors are predominantly found in the central nervous system, particularly in the brain, while CB2 receptors are more dispersed throughout peripheral tissues and immune cells. These receptors serve as crucial gatekeepers, receiving signals from endocannabinoids and phytocannabinoids alike.
The connection between the ECS, brain receptors, and the nervous system is a tightly woven tapestry that regulates various physiological processes. CB1 receptors, abundant in areas associated with cognitive functions, play a pivotal role in modulating neurotransmitter release, impacting phenomena such as mood, memory, and pain perception. On the other hand, CB2 receptors, more prevalent in the immune system, influence inflammation and immune responses.
In the Canadian context, the impact of cannabis on CB1 and CB2 receptors holds particular significance due to the country’s evolving cannabis landscape. With the legalization of cannabis, individuals have gained increased access to a variety of cannabis products, each carrying distinct ratios of cannabinoids. The interplay between these cannabinoids, particularly THC and CBD, with CB1 and CB2 receptors, influences the psychoactive and therapeutic effects of cannabis. Understanding this interplay is essential for consumers navigating the Canadian cannabis market, as it allows for informed choices based on the desired outcomes, whether recreational or medicinal, in alignment with the unique properties of different cannabis strains and products available.
Biological Functions Regulated by ECS
The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) extends its regulatory influence across a spectrum of crucial biological functions, acting as a silent orchestrator behind the scenes. ECS’s impact on various bodily functions is profound, encompassing mood regulation, immune response, sleep patterns, and more. One area where the ECS plays a pivotal role is in the modulation of eating habits. The intricate dance between endocannabinoids and receptors, particularly CB1, has been linked to the regulation of appetite and the rewarding aspects of food consumption. This connection highlights the ECS’s involvement not only in maintaining physiological balance but also in shaping behaviors related to nutrition.
Canadian research has made significant strides in unraveling the intricate relationship between the ECS and various biological functions. With the progressive legalization of cannabis in Canada, there has been a surge in scientific exploration to understand how cannabinoids interact with the ECS and impact health. Studies have delved into the specific nuances of ECS modulation in the Canadian population, shedding light on the potential therapeutic applications for conditions related to appetite dysregulation, such as those associated with certain medical treatments. This burgeoning field of research underscores the importance of staying abreast of scientific developments, especially for individuals navigating the Canadian cannabis market, as it opens new avenues for utilizing cannabis as a tool for promoting holistic well-being.
ECS and Mental Health
The intricate relationship between the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) and mental health represents a significant frontier in cannabis research, particularly in the Canadian context. Exploring the link between ECS and anxiety reveals a nuanced interplay wherein endocannabinoids, when in balance, may contribute to stress resilience. CB1 receptors, abundant in areas of the brain associated with emotional processing, play a key role in modulating anxiety responses. Understanding this dynamic can offer insights into how cannabis, with its potential to influence the ECS, may impact anxiety-related conditions.
The ECS’s role in memory and learning processes adds another layer to its influence on mental health. CB1 receptors are prevalent in brain regions responsible for memory formation and cognitive functions. The modulation of neurotransmitter release by the ECS suggests its involvement in shaping memory consolidation and learning experiences. This intricate dance within the ECS underscores its potential impact on cognitive functions, a factor of paramount importance in mental well-being.
Canadian studies have been pivotal in advancing our understanding of cannabis and mental health within the framework of the ECS. With the legalization of cannabis, there has been a surge in research examining the therapeutic potential and potential risks associated with cannabis use, particularly concerning mental health outcomes. These studies delve into how cannabinoids, by interacting with the ECS, may influence conditions such as anxiety disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and depression. Navigating the Canadian cannabis landscape necessitates a nuanced understanding of these findings, allowing individuals to make informed choices based on their mental health needs while considering the complexities of the ECS modulation.
Metabolism and Reproduction in the Context of ECS
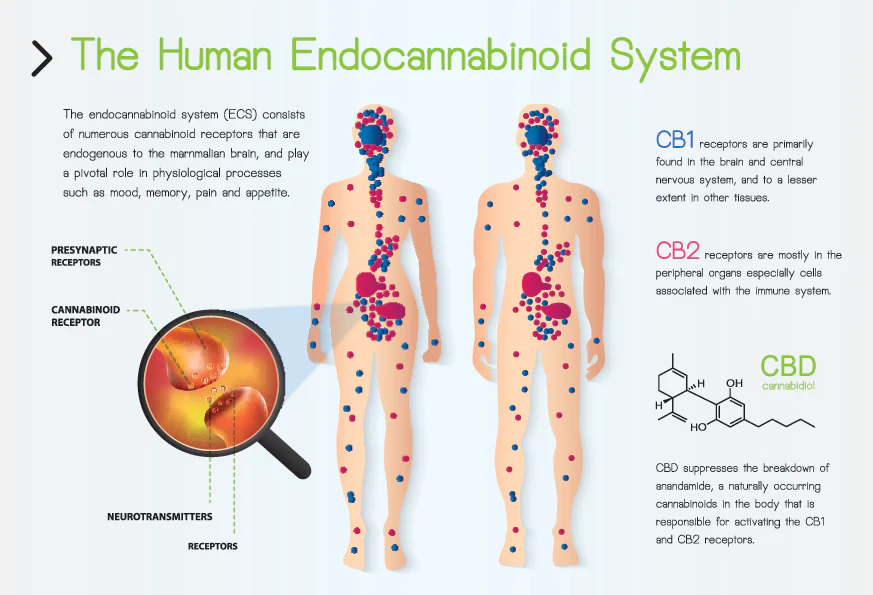
Within the intricate web of the Endocannabinoid System (ECS), its influence extends to two critical aspects of human physiology: metabolism and reproduction. The ECS plays a pivotal role in regulating metabolism, acting as a fine-tuner in the intricate balance of energy homeostasis. This regulatory function is particularly evident in the ECS’s impact on appetite, nutrient utilization, and energy storage, with CB1 receptors, abundantly present in the central nervous system, influencing these processes. Understanding the ECS’s role in metabolism is key for those navigating the Canadian cannabis market, as different strains and cannabinoid profiles may have varying effects on appetite and overall metabolic health.
In addition to metabolism, the ECS intricately influences reproductive functions. The presence of ECS components in the reproductive organs and the modulation of endocannabinoids during different stages of the reproductive process highlight the system’s role in fertility and pregnancy. This dual role of the ECS in both metabolism and reproduction underscores its pervasive impact on fundamental aspects of human biology.
In the Canadian cannabis market, the relevance of the ECS concerning metabolism and reproduction is substantial. As individuals explore cannabis for various reasons, including wellness and recreation, understanding how different cannabinoids interact with the ECS becomes paramount. This awareness empowers consumers to make informed choices aligned with their health goals. Moreover, as research in Canada continues to unfold, elucidating the intricate links between the ECS, cannabis, metabolism, and reproduction, individuals can anticipate an evolving landscape where tailored cannabis products may address specific needs related to these physiological processes.
Harnessing the Benefits: Practical Tips for Cannabis Consumers
For cannabis consumers in Canada, optimizing the benefits of cannabis while ensuring a balanced Endocannabinoid System (ECS) requires a nuanced approach. Understanding the optimal use of cannabis for ECS balance involves recognizing the unique interplay between cannabinoids, particularly THC and CBD, and individual physiological responses. Striking a balance that aligns with personal wellness goals and preferences is crucial. Dos and don’ts for maintaining a healthy ECS involve mindful consumption, recognizing the importance of moderation, and being cognizant of individual tolerance levels. It’s essential to avoid excessive or imbalanced cannabis use, as this can potentially disrupt the delicate equilibrium within the ECS.
In the diverse landscape of the Canadian cannabis market, consumers have access to an array of products tailored to address specific ECS needs. From CBD-dominant products for those seeking non-psychoactive relief to balanced THC:CBD ratios catering to a more holistic experience, the market caters to a variety of preferences. Education plays a pivotal role in helping consumers navigate this expansive market, empowering them to make informed decisions about product selection, consumption methods, and dosage. As regulations evolve and scientific understanding deepens, the Canadian cannabis market is poised to offer increasingly specialized products, providing consumers with more options to tailor their cannabis experience in alignment with ECS health.
Individualized Approaches to ECS Optimization
As we delve into the intricacies of the Endocannabinoid System (ECS), it becomes evident that individual responsiveness to its modulation varies significantly. Exploring these variations in ECS responsiveness among individuals reveals a personalized dimension to cannabis consumption. The ECS, influenced by genetics, lifestyle, and environmental factors, manifests differently in each person, impacting how they respond to cannabinoids. Tailoring cannabis consumption based on personal ECS profiles acknowledges this diversity, emphasizing the need for a nuanced approach to optimize individual well-being.
Understanding one’s unique ECS responsiveness enables consumers in Canada to make informed choices about the type, concentration, and method of cannabis consumption that aligns with their specific physiological makeup. This individualized approach not only enhances the potential therapeutic benefits of cannabis but also contributes to a more satisfying and personalized cannabis experience, reflecting the diverse needs and preferences within the Canadian population. As the Canadian cannabis market continues to evolve, the potential for personalized cannabis experiences is increasingly recognized, offering consumers the opportunity to navigate and enjoy the benefits of cannabis in a way that resonates uniquely with their own ECS characteristics.
Challenges and Controversies
Despite the burgeoning interest and advancements in the understanding of the Endocannabinoid System (ECS), challenges and controversies persist, shaping the discourse around its role in cannabis consumption. Common misconceptions about the ECS often stem from a lack of awareness and can lead to misinformation. One such misconception is oversimplifying the ECS’s functions, overlooking its intricate interplay in maintaining homeostasis across various bodily systems. Clearing these misconceptions is crucial for fostering a more accurate understanding of the ECS and its implications.
Controversies surrounding the ECS and cannabis further contribute to the nuanced landscape. Debates often revolve around the therapeutic potential versus potential risks associated with cannabis use, especially concerning mental health. Questions about the long-term effects of cannabis on the ECS and its role in certain medical conditions continue to fuel discussions within the scientific and medical communities. Addressing these controversies requires ongoing research and open dialogue to navigate the complexities and provide evidence-based insights.
In the Canadian context, legal aspects add an additional layer of complexity to ECS-related cannabis consumption. With the legalization of recreational cannabis, regulations continue to evolve, impacting the accessibility and usage of cannabis products. Understanding the legal framework surrounding the ECS and cannabis is vital for consumers, ensuring compliance with Canadian laws. As policies adapt, staying informed about legal implications becomes paramount for individuals seeking to integrate cannabis into their wellness routines, contributing to a more responsible and legally compliant cannabis landscape in Canada.
Future of ECS Research in Canada
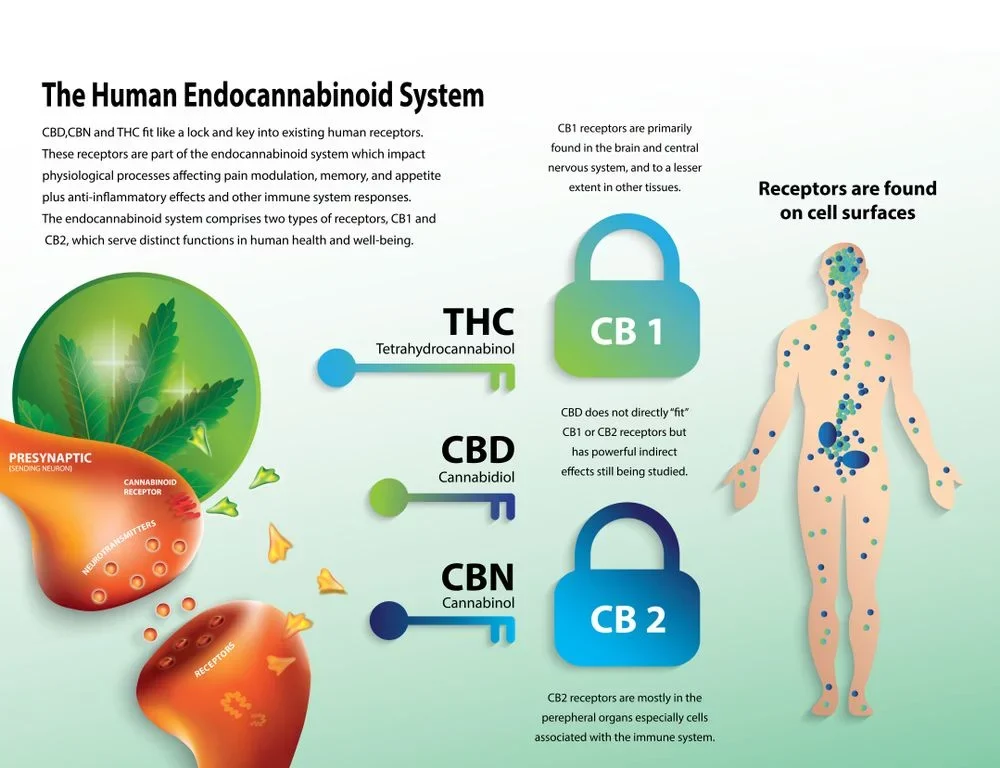
The future of Endocannabinoid System (ECS) research in Canada holds great promise, as scientists delve into emerging trends and studies that continue to unveil the intricacies of this complex physiological system. Research is increasingly focusing on unraveling novel aspects of the ECS, exploring its role in specific health conditions, and understanding the potential therapeutic applications of cannabinoids. The emergence of cutting-edge technologies and methodologies is facilitating a deeper dive into the ECS, allowing for more precise insights into its functions and interactions.
The potential impact of ECS knowledge on the Canadian cannabis industry is substantial. As research elucidates the nuances of how cannabinoids interact with the ECS, the industry can anticipate more targeted and personalized cannabis products. This shift towards precision in product development has the potential to revolutionize the therapeutic landscape, offering consumers tailored solutions for their specific health and wellness needs. The Canadian cannabis market may witness a transformation with the integration of ECS-centric insights, fostering the development of innovative products that cater to diverse consumer preferences and health goals.
Encouraging further exploration and advancements in ECS understanding is paramount for continued growth and development. By supporting and promoting ongoing research initiatives, stakeholders in Canada can contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the ECS’s role in human health. This encouragement facilitates the generation of valuable knowledge that not only informs medical practices but also shapes responsible cannabis use. As the scientific community and the cannabis industry collaboratively push the boundaries of ECS research, Canadians can anticipate a future where cannabis products are not only legalized but optimized for the promotion of holistic well-being based on a deep understanding of the ECS and its intricate functions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, our exploration of the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) has underscored its paramount significance in the context of cannabis consumption for individuals in Canada. As a complex network of receptors, endocannabinoids, and enzymes, the ECS plays a crucial role in maintaining balance within the body, influencing various biological functions and mental processes. From its impact on brain receptors, regulation of biological functions, and involvement in mental health to its role in metabolism and reproduction, the ECS is a dynamic system that intertwines with the diverse facets of human physiology.
Encouraging continued education and research in the field is pivotal for both consumers and industry stakeholders alike. As the Canadian cannabis landscape evolves, staying abreast of emerging trends and scientific insights surrounding the ECS ensures that individuals can make informed decisions about their cannabis consumption. This ongoing research not only deepens our understanding of the ECS but also contributes to the development of safer and more effective cannabis products tailored to individual health needs.
Reiterating the importance of a balanced ECS for overall well-being becomes a central tenet. With the legalization of cannabis, individuals have unprecedented access to a variety of products, each with its unique cannabinoid profile. Striving for a balanced ECS through mindful cannabis consumption aligns with the goal of promoting holistic wellness. As consumers navigate the expanding array of cannabis options in Canada, maintaining a nuanced understanding of the ECS and its intricate interplay with cannabinoids remains key to unlocking the potential benefits of cannabis for individual health and well-being.





